

In recent years the ESP8266 has become one of my go-to choices for smart home/IoT devices or projects requiring WiFi. It is cheap (around $1.5 on Amazon)1, has WiFi, and can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, making it an easy replacement for Arduinos if we need WiFi connectivity.
This post outlines the most important guidlines when designing a pcb for an ESP8266 module. It is part of a complete ESP8266 reference you can find here.
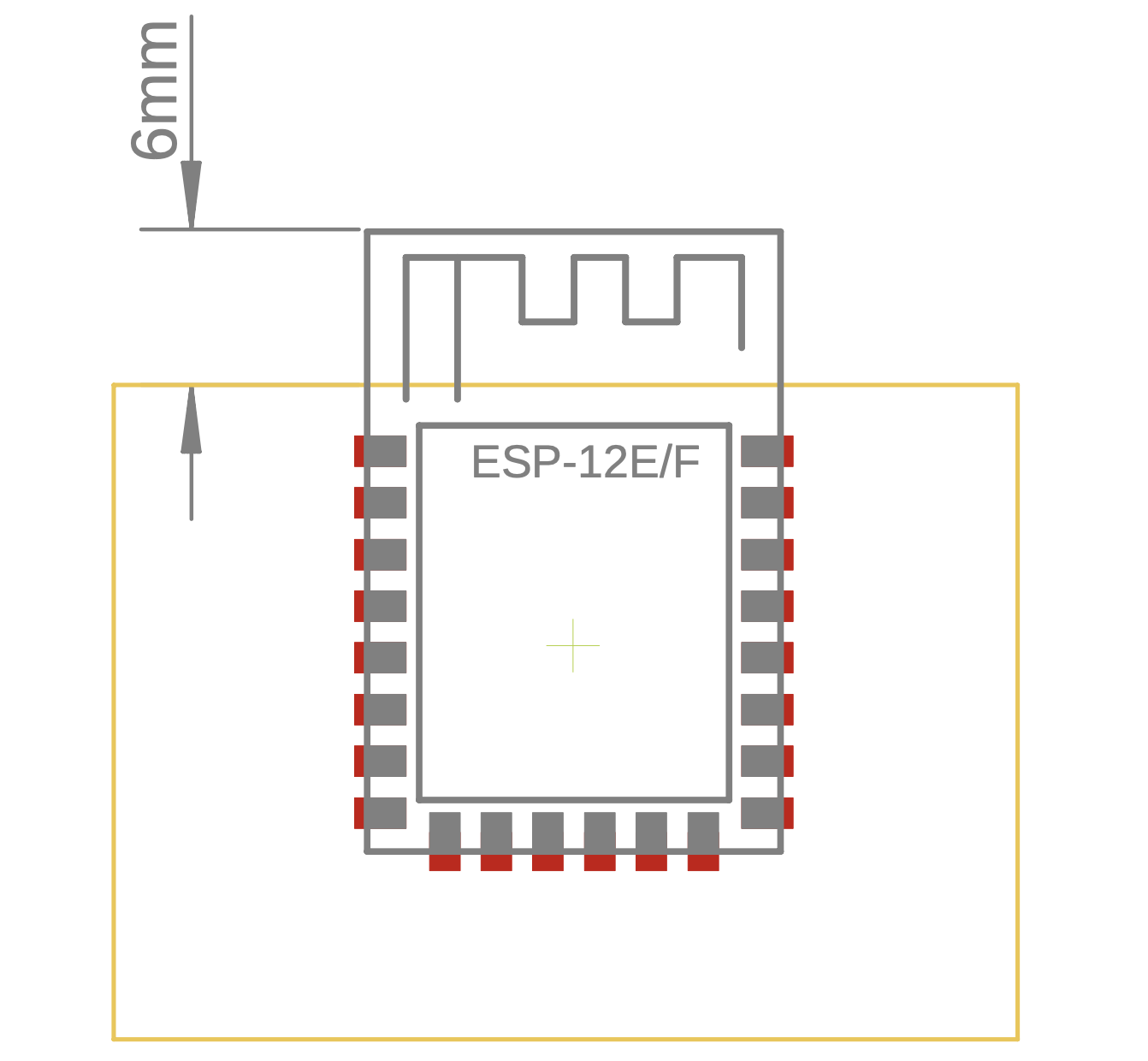
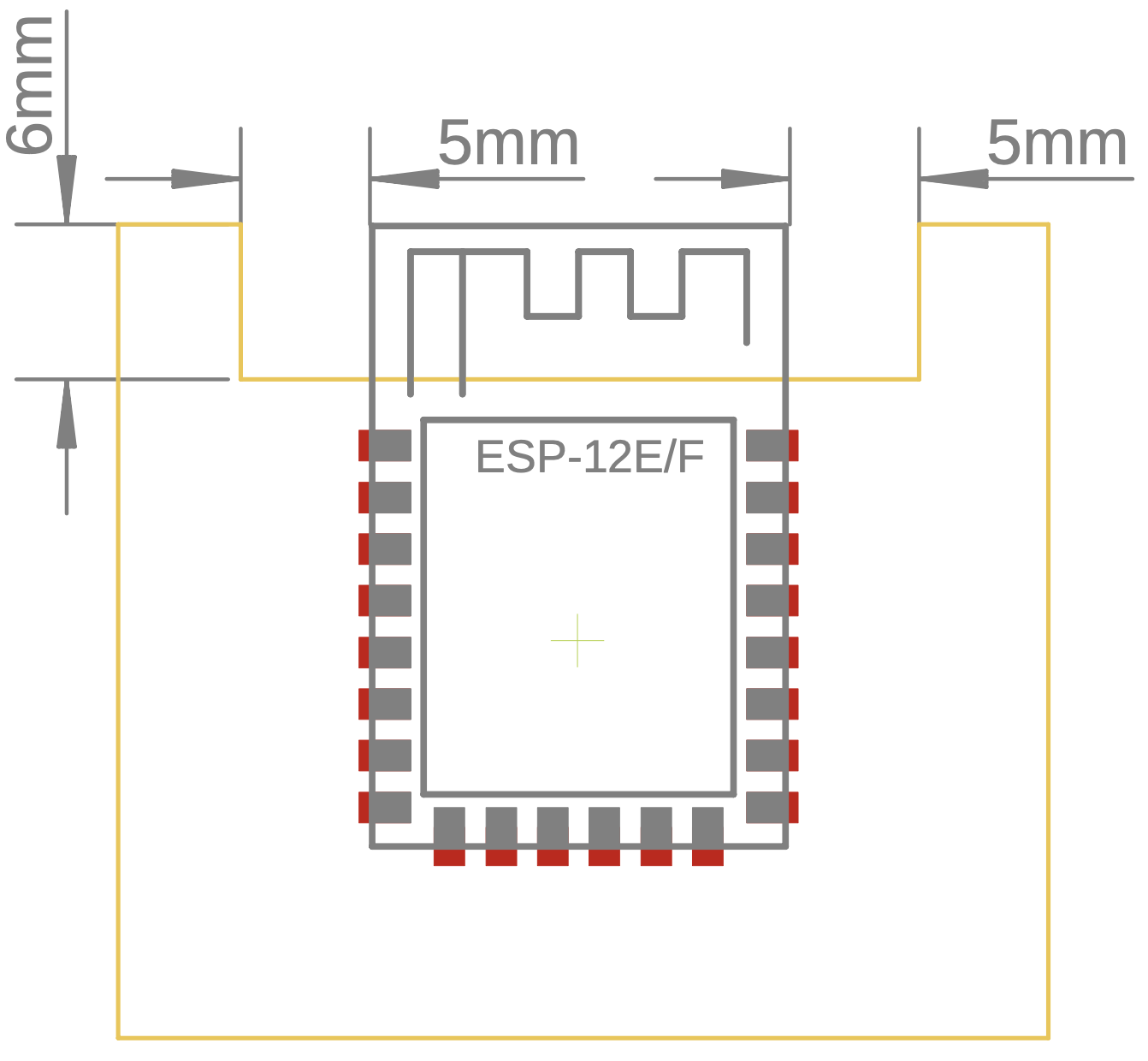
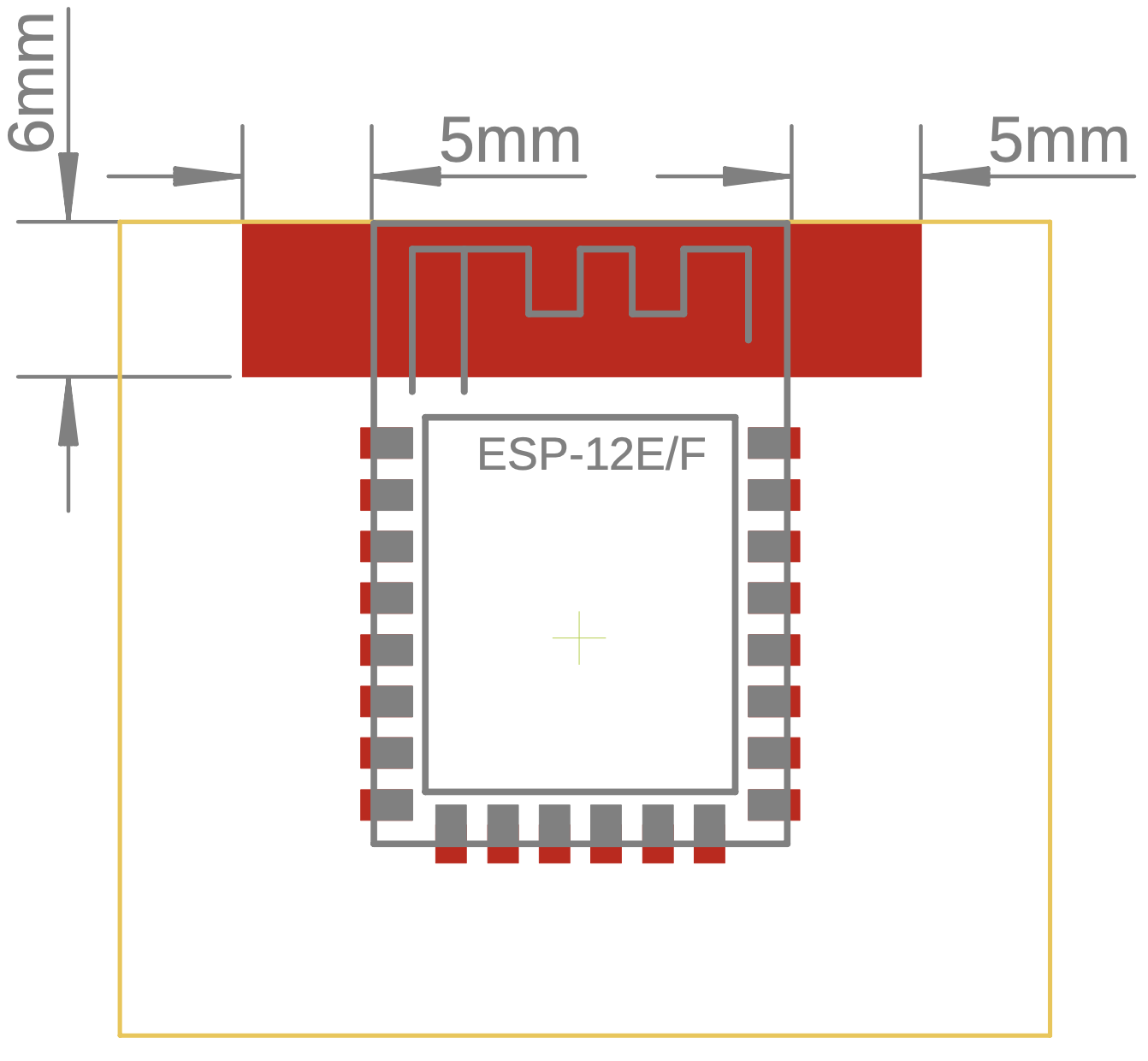
Espressif provides a hardware design guide for free. Noticeable takeaways are that we want to place the antenna of the esp module outside of our PCB or, if this is not possible, at least 15mm away from other components (keep-out zone). Meanwhile, [10] only shows a 5mm keep-out zone, as depicted in Fig. 6.1 (c) below. According to [1], we also want to avoid using resistors larger than 2.2k near the esp module as they might be affected by the WiFi. Up to 2.2kOhm seem to work without issues.
This post is part of a complete ESP8266 reference/guide. You can find more information on how to use your ESP8266 module effectively at blog.hirnschall.net/esp8266/.

The content published on this page (with exceptions) is published under the CC Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported License. You are free to share on commercial blogs/websites as long as you link to this page and do not sell material found on blog.hirnschall.net/* or products with said material.
1: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.